Eye Condition
Diabetic Retinopathy
Diabetic retinopathy develops when high blood sugar damages retinal blood vessels, causing blurry vision, floaters, and potentially permanent vision loss.
Explore our treatment options for Diabetic Retinopathy
What Is Diabetic Retinopathy?
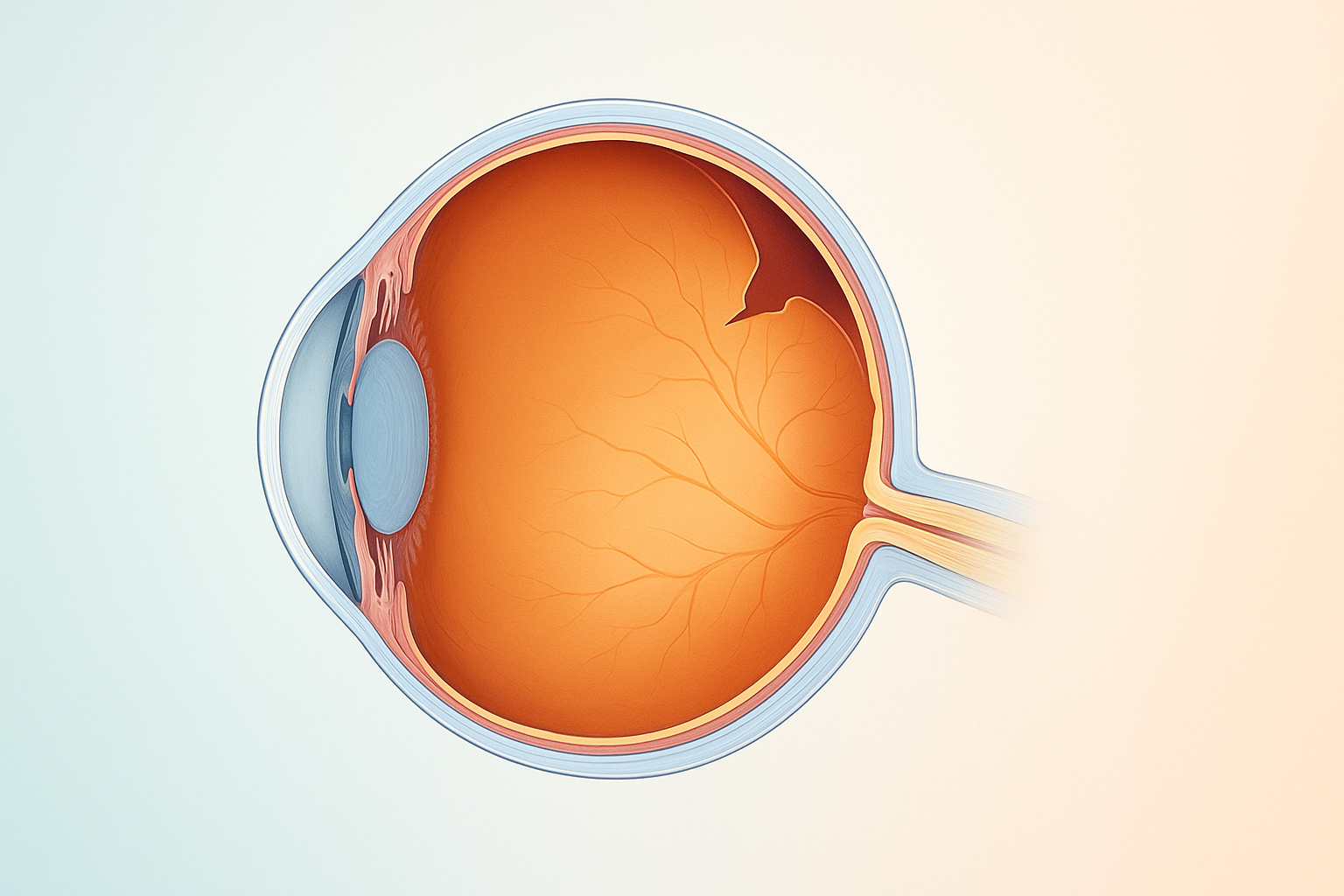
Diabetic retinopathy (DR) is the most common diabetes-related eye disease. Persistently high blood-sugar levels weaken and leak the tiny blood vessels that nourish the retina, the light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye. Left unchecked, this leakage and the growth of fragile new vessels can scar the retina and threaten central vision.
How Diabetes Damages the Retina
- Blood sugar spikes stress retinal vessels, causing them to swell and leak.
- Insulin resistance or deficiency leaves excess glucose in the bloodstream, accelerating vascular breakdown.
- Fluid accumulation and fragile new vessels block or distort the macula, the center of sharp vision.
- Retinal edema and hemorrhages raise the risk of sudden vision loss or retinal detachment.
Early Signs & Symptoms
- Blurry or fluctuating vision
- Dark floaters or spots
- Difficulty reading or seeing at night
- Empty or dark areas in your field of view
Many patients notice no symptoms until damage becomes advanced, so routine eye exams are critical.
Who is Most at Risk?
- Individuals using insulin or diabetes medications
- Patients with poorly controlled A1C levels
- People with long-standing type 1 or type 2 diabetes
- Anyone who skips routine dilated eye exams
Proven Ways to Protect Your Vision
- Keep blood sugar within your target range through diet, exercise, and prescribed medication.
- Monitor A1C levels and aim for stable daily readings.
- Control blood pressure and cholesterol to reduce vascular stress.
- Schedule comprehensive dilated eye exams at least once a year.
Treatment Options Available at Eye Health Institute
Dr. Andy Rosenfarb combines conventional and integrative care to stabilize vision quickly:
- Anti‑VEGF injections to stop abnormal vessel growth and reduce swelling.
- Focal or grid laser therapy to seal leaking microaneurysms.
- Vitrectomy surgery for persistent bleeding or retinal detachments.
- Supportive therapies such as acupuncture, alternating-current stimulation, targeted supplements, personalized diet plans, exercise guidance, and hyperbaric oxygen sessions.
Clinical results: Diabetic retinopathy is often the fastest-improving retinal condition treated at our clinic, with measurable gains in vision and vascular health when patients follow the full program.
Key Takeaway
Consistent blood sugar control, healthy lifestyle habits, and timely retinal care allow most people with diabetic retinopathy to maintain clear sight and avoid preventable blindness.